

It affects the trunk, limbs, palms and soles, and usually spare the face, scalp and mouth. A rash is present in the majority of patients with disseminated gonococcal infection. What are the cutaneous manifestations of gonorrhoea?Īlthough gonorrhoea usually affects the mucosal surfaces, it may also affect the skin. Very rare complications of gonococcal infection include meningitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis and vasculitis. Risk factors for disseminated gonococcal infection include recent menstruation, complement deficiencies, systemic lupus erythematosus and microbial factors specific to some strains of the bacteria (eg, porin B isoform 1 A of the bacterial outer membrane). Constitutional symptoms (such as fever, chills and malaise).Polyarthralgia and oligoarthralgia, or purulent arthritis.It occurs in 0.5–3% of infected individuals. Disseminated gonococcal infectionĭisseminated gonococcal infection results from the spread of the bacteria to the joints and other tissues. Conjunctival gonococcal infection can result in scarring, permanent visual impairment and blindness. Conjunctival infectionĪdult conjunctivitis can occur from auto- inoculation and is less common than neonatal conjunctivitis. Vertical transmission from mother to child can cause neonatal conjunctivitis and, more rarely, bacterial sepsis. Gonococcal infection during pregnancy can result in miscarriage, preterm delivery and postpartum endometritis. Ascending infection in malesĪscending infection in males can cause painful inflammation and swelling of the epididymis and the testicles (epididymo-orchitis). Scarring of the female upper genital tract can lead to chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy and infertility. Ascending infection in femalesĪscending infection in females can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (endometritis, salpingitis, tubal-ovarian abscess). This is more likely to occur when the infection is asymptomatic or when there is any barrier to access health care. What is disseminated gonococcal infection?Ĭomplications of gonorrhoea occur when the infection is left undiagnosed and untreated. Pharyngeal infection is becoming increasingly common particularly in men who have sex with men (MSM) and is largely asymptomatic. Anal discomfort and discharge due to proctitis.Tender periurethral glands and Bartholin glands.
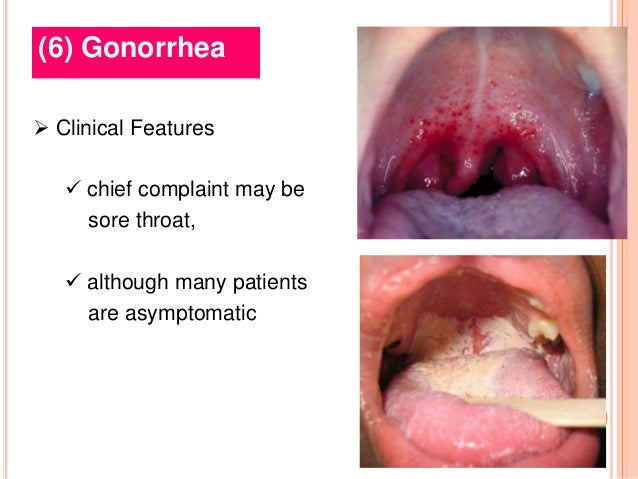
Lower abdominal pain which may be due to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).Anal discomfort and discharge due to proctitis).Testicular discomfort and swelling due to epididymo- orchitis.Urethral discharge (often mucopurulent).The clinical features of localised gonorrhoea are different between males and females Males Gonorrhoea is asymptomatic in 10–15% of men and in up to 80% of women. The incubation period is on average two to seven days. What are the signs and symptoms of gonorrhoea? Safer sex means using a condom or oral dam during sexual activity, which may include vaginal, oral or anal contact. People at risk of gonorrhoea are mainly sexually active people that come in contact with an infected person while not practising safer sex. If the mother is infected, gonorrhoea may also be passed to a newborn delivered vaginally causing conjunctivitis.

Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The common sites of infection are the mucous membranes of the urethra, endocervix, rectum, pharynx and conjunctiva. doi:10.3201/eid2201.Gonorrhoea is a disease is due to infection with the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi infections. González-beiras C, Marks M, Chen CY, Roberts S, Mitjà O. Scabies frequently asked questions ( FAQs). Scabies (Sarcoptes Scabiei).Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Final recommendation statement: syphilis infection in pregnant women: Screening. Final recommendation statement: chlamydia and gonorrhea: screening. Management and treatment of cervicitis: A review of clinical effectiveness and guidelines. Trends in adult chlamydia and gonorrhea prevalence, incidence and urethral discharge case reporting in morocco over 1995-2015-estimates using the spectrum-sexually transmitted infection model. HPV and men - fact sheet.Įl-kettani A, Mahiané G, Bennani A, et al.

doi:10.1001/jama.2018.20181Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021: g enital herpes.Īmerican Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Genital herpes (HSV-2).Ĭenters for Disease Control and Prevention. Herpes virus, oral clinical signs and QoL: systematic review of recent data. The presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of sexually transmitted infections. Wagenlehner FM, Brockmeyer NH, Discher T, Friese K, Wichelhaus TA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
